The human circulatory system consists of three main components: the blood, the heart, and the blood vessels. The circulatory system's job is to transport substances around the body. The cells in the body require a constant input of oxygen and nutrients and a continuous removal of carbon dioxide and other wastes.
The circulatory system has three main components:
Blood
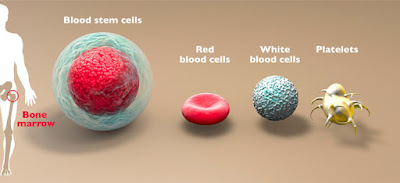
There are four components of blood:
- Red Blood Cells - transport oxygen throughout the body, using hemoglobin.
- White Blood Cells - the infection fighters.
- Platelets - aid in blood clotting
- Plasma - liquid that carries the blood cells along.
Heart
There are three main components of the heart:
- Cardiac Muscle Tissue - makes the heart contract and moves blood around the body.
- Nerve Tissue - transmits signals to and from the central nervous system.
- Connective Tissue - contributes to structure and function.
 |
| Cardiac muscle tissue under the microscope. |
Blood Vessels
There are three types of blood vessels:
- Arteries - carry blood away from the heart.
- Veins - carry blood toward the heart.
- Capillaries - tiny blood vessels that allow substances to diffuse between blood and body fluids/tissues.
 |
| Artistic rendering of blood vessels. |
Time to make like the circulatory system and start pumping out some work.